Raw Material
• Billet
Steel billets result from the second stage of the steel production process. They are hot-rolled or square inches. forged from an ingot or strand cast. Smaller and longer than a bloom, billets are usually a square cross section less than 36 They are used for the manufacture of all 'long' steel products such as bars, rods, pipes, tubes, wire and wire products.
130 mm, 150 mm, 165 mm, 200 mm, 250 mm squares, Length - upto 13 metres

• Blooms
Blooms are hot-rolled or forged from an ingot or strand cast. They usually have a square cross section exceeding 36 square inches. They are mainly used in the manufacture of ‘long’ products such as structural shapes, structural profiles, building beams, rails and columns.
285 mm x 390 mm and 280 mm x 320 mm rectangle

• Cast Iron
Cast iron an iron alloy that contains high amounts of carbon. It is a raw material for the production of new steel and cast-iron products. The steelmaking and foundry industries are dependent upon the ready availability of cast iron from manufacturing operations and from the recovery of products that are no longer used or needed. Cast iron is very strong, dense and malleable iron alloy. Cast iron is the primary product of ferrous metallurgy and it is used for repartition in steel production. It is one of the basic
constructional materials. Cast iron is widely used in mechanical engineering because of its good casting and durability properties. What concerns durability, it competes only with carbonaceous steel. In modern mechanical engineering almost 75% of extracted cast iron is used in machinery and various metallic products.
With its low melting point, good fluidity, excellent malleability and wear resistance cast irons have become an engineering material with a wide range of applications, like: water waste hatches, lattices, sewer pipes, huge main water pipes and other similar big, heavy and durable stuff.

• Coal/Coke
Iron ore is the raw material required to make pig iron, which is the primary (98%) raw material used to make steel. Pure iron ore is virtually unknown on the surface of the Earth except as Fe-Ni alloys from meteorites and very rare forms of deep mantle xenoliths. Therefore, all sources of iron used in industry exploit iron oxide minerals, one of the primary forms of which is hematite. World resources of iron ore are estimated to exceed 800 billion tonnes of crude ore containing more than 230 billion tonnes of iron, implying an average iron content of 28.75%.Iron ore consists of oxygen and iron atoms bonded together to form the iron-oxide molecule and needs to have the oxygen removed through smelting to create a purer iron product. During this process, the iron ore is heated to extreme temperatures in blast furnaces where lump ore is more stable and therefore preferred. By comparison, iron fines must be sintered before charging to the furnace. The premium associated with lump ore has persisted historically, reflecting the approximate costs required to sinter iron fines, the availability of furnaces required and other benefits including ease of transportation.

• Iron Ore
Iron ore is the raw material required to make pig iron, which is the primary (98%) raw material used to make steel. Pure iron ore is virtually unknown on the surface of the Earth except as Fe-Ni alloys from meteorites and very rare forms of deep mantle xenoliths. Therefore, all sources of iron used in industry exploit iron oxide minerals, one of the primary forms of which is hematite. World resources of iron ore are estimated to exceed 800 billion tonnes of crude ore containing more than 230 billion tonnes of iron,
implying an average iron content of 28.75%.Iron ore consists of oxygen and iron atoms bonded together to form the iron-oxide molecule and needs to have the oxygen removed through smelting to create a purer iron product. During this process, the iron ore is heated to extreme temperatures in blast furnaces where lump ore is more stable and therefore preferred. By comparison, iron fines must be sintered before charging to the furnace. The premium associated with lump ore has persisted historically, reflecting the approximate costs required to sinter iron fines, the availability of furnaces required and other benefits including ease of transportation.

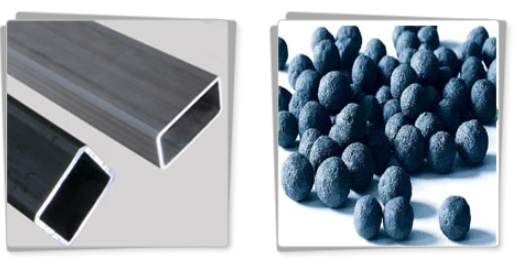
• Iron Ore Pellet
Iron ore pellets are indurated, spheres of ore with a high iron content and uniform quality. Peller plants can produce two varieties of pellets: blast furnace pellets and direct reduction pellets (DR pellets). Blast furnace pellets are used in the coke-based blast furnace process, which is the most common method of producing hot metal (molten iron for steelmaking). Blast furnace pellets are delivered mainly to steel mills. DR pellets are used in the direct reduction processes to produce sponge iron, which is an alternative process route, as an initial stage from iron to steel. The DR process is primarily based on the use of natural gas and has become increasingly common in countries with access to inexpensive natural gas.
• Ingots
The steel ingots, stainless steel ingots, industrial steel ingots, stainless steel ingot bars are manufactured using deep processing such as hot bundling, forging, cold bundling, etc. They are widely used for making wires and sheets. They are available in standard sizes and shapes and are tested on different quality parameters before supplying them to the customer We offer our client an excellent quality range of Stainless Steel Ingots, which are manufactured from high grade quality raw materials. These Stainless Steel Ingots can be customized as per our precious customers specifications. These Stainless Steel Ingots are widely known for its durability and quality. Our Stainless Steel Ingots can be availed at industrial leading price.

• Metallics (DRI,HBI,Pig Iron)
India is also an important producer of pig iron. Post-liberalization, with setting up several units in the private sector, not only imports have drastically reduced but also India has turned out to be a net exporter of pig iron. The private sector accounted for 91% of total production for sale of pig iron in the country in 2011-12. The production of pig iron has increased from 1.6 mt in 1991-92 to 5.78 mt in 2011-12. Our Trade in basic pig iron for steelmaking, as well as foundry and ductile pig iron for the castings industry.
Direct reduced iron that has been processed into briquettes. Instead of using a blast furnace, the oxygen is removed from the ore using natural gas and results in a substance that is 90%-92% iron. Because DRI may spontaneously combust during transportation, HBI is preferred when the metallic material must be stored or moved Hot Briquette Iron (HBI) is a relatively new product, developed in the past 25 years, as a supplement for pig iron and scrap in electric furnace steel mills. It is a compacted form of direct reduced iron (DRI), which facilitates its handling, storage, and use. 
• Slabs
Steel slabs are hot-rolled from an ingot or strand cast. They are wide and rectangular in shape. They are used for the manufacture of all 'flat' steel products such as coils, sheets, strip, plates and other flat-rolled steel products.

• Scrap
If you have scrap to buy, then look no further. There are a number of reasons why buying from Tirupati is the best option for you. We pride ourselves on our customer service and place great importance on finding the right solution for each individual customer. We look for long term partnerships, and believe our audit proven methods will offer your company unrivalled opportunities to increase its returns from scrap metals. What’s more we guarantee that the prices we take are always very competitive.

• Sponge Iron
India is the world’s largest producer of sponge iron with a host of coal based units, located in the mineral-rich states of the country. Over the years, the coal based route has emerged as a key contributor and accounted for 76% of total sponge iron production in the country (20.37 mt in 2011-12; prov.). Capacity in sponge iron making too has increased over the years and stands at around 35 mt.
Sponge Iron is a metallic product formed by the reduction of iron ore at temperature just below the fusion point of iron. This product has derived the name "Sponge Iron" due to its porous nature.
